Introduction
Fluorine, the ninth element of the periodic table, captivates scientists with its unparalleled reactivity and transformative applications. How many valence electrons does fluorine have? This question unlocks the secret behind its chemical vigor, driving its role in everything from toothpaste to rocket fuel. Discovered in the 19th century after decades of perilous experiments, fluorine’s story blends danger and discovery. As of April 2025, its applications in medicine, industry, and environmental science underscore its importance. This article explores fluorine’s history, properties, uses, and biological significance, revealing why this element shapes our world.

History of Discovery
Fluorine’s discovery was a triumph of persistence amid hazardous challenges. In the early 1800s, chemists recognized fluorine’s presence in minerals like fluorite (CaF₂) but struggled to isolate it due to its extreme reactivity. Humphry Davy, in 1813, attempted electrolysis but was poisoned by fluorine gas. Several chemists, including Joseph Gay-Lussac, suffered severe injuries from its corrosive nature. It was not until 1886 that Henri Moissan succeeded, using electrolysis of potassium bifluoride in anhydrous hydrogen fluoride to isolate fluorine gas. Moissan’s breakthrough earned him the 1906 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
The isolation of fluorine marked a turning point in chemical science. Its name, derived from the Latin “fluere” (to flow), reflects its role in flux materials like fluorspar. By the early 20th century, fluorine’s reactivity intrigued researchers, leading to studies of its electron structure. For example, its position in group 17 (halogens) hinted at its chemical behavior. Moissan’s work paved the way for modern applications, from fluorides in dentistry to fluoropolymers in industry, establishing fluorine as a cornerstone of chemistry.

Chemical Properties
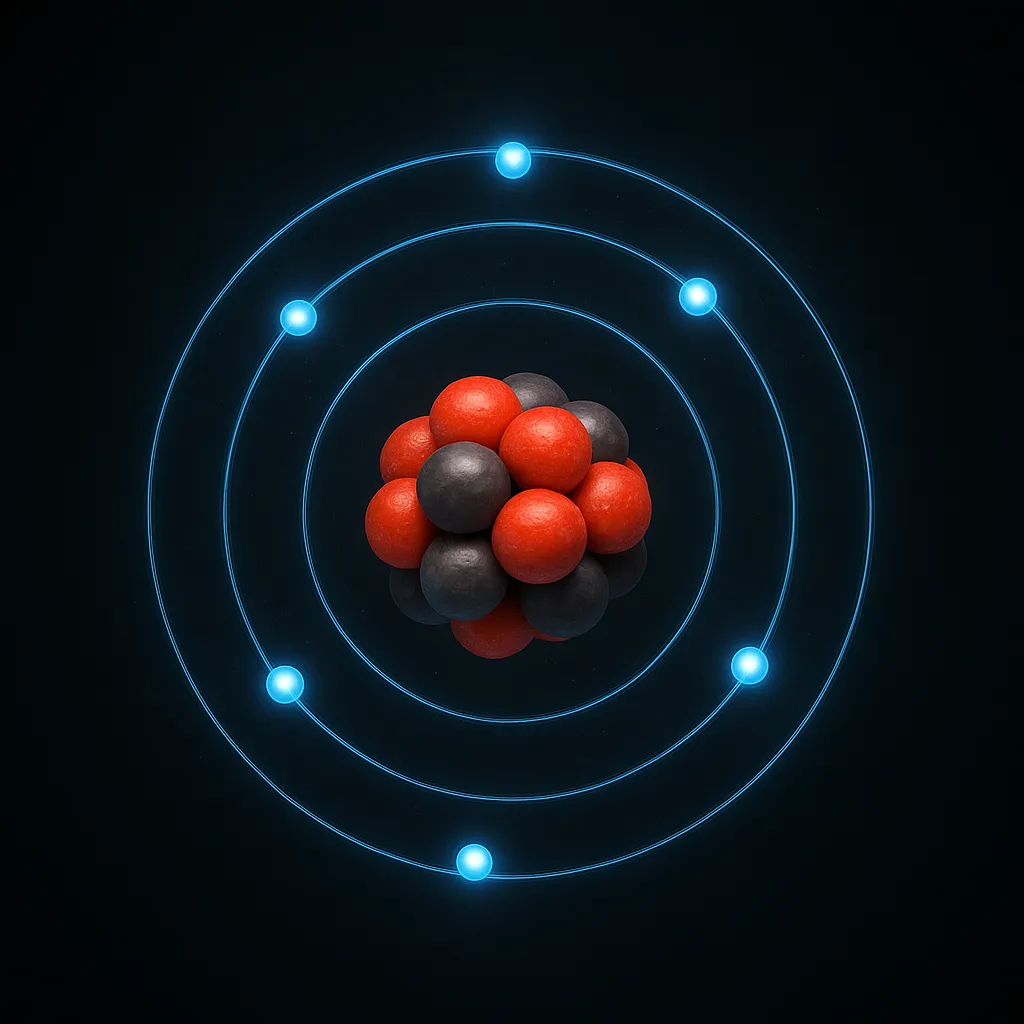
Fluorine’s extraordinary properties stem from its atomic structure. How many valence electrons does fluorine have? Fluorine, with an atomic number of 9, has 7 valence electrons in its 2s²2p⁵ configuration, making it highly electronegative (3.98 on the Pauling scale). This electron arrangement drives its tendency to form single bonds by gaining one electron, achieving a stable octet. How many valence electrons does fluorine have in its compounds? In molecules like HF or F₂, it maintains its 7 valence electrons but shares or gains one to form bonds.
Fluorine exists as a pale yellow, diatomic gas (F₂) at room temperature, with a boiling point of -188.1°C and a melting point of -219.6°C. Its small atomic radius (72 pm) enhances its reactivity, as electrons are tightly held, creating strong electrostatic attraction. For instance, fluorine reacts vigorously with most elements, including noble gases like xenon, forming compounds like XeF₂. Its corrosiveness requires specialized handling, using materials like nickel or PTFE. These properties, rooted in its electron structure, make fluorine the most reactive element in the periodic table.

Applications
Fluorine’s reactivity enables a wide range of applications across industries. How many valence electrons does fluorine have in its industrial role? Its 7 valence electrons underpin its ability to form stable compounds like fluorides and fluoropolymers. In medicine, fluoride ions (F⁻) strengthen tooth enamel, reducing cavities by 25% in fluoridated water systems, as reported by the CDC in 2024. Fluorine-18, a radioactive isotope, is used in PET scans, with over 2 million scans annually worldwide.
In industry, fluorine is critical for producing polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known as Teflon, discovered in 1938 by Roy Plunkett. PTFE’s non-stick properties revolutionize cookware and industrial coatings. Fluorine also enhances uranium hexafluoride (UF₆) for nuclear fuel enrichment, supporting 10% of global electricity via nuclear power. In electronics, fluorine-based plasma etching shapes silicon wafers for microchips, enabling 5 nm semiconductor nodes by 2025. Additionally, fluorinated gases like SF₆ are used in high-voltage insulation, though their environmental impact raises concerns. These applications highlight fluorine’s versatility, driven by its chemical properties.
Biological and Environmental Significance
Fluorine plays a dual role in biology and the environment, offering benefits and challenges. How many valence electrons does fluorine have in biological contexts? Its 7 valence electrons facilitate the formation of fluoride ions, which integrate into hydroxyapatite in teeth and bones, enhancing durability. The World Health Organization notes that 1 ppm fluoride in water prevents dental caries, benefiting 400 million people globally. However, excessive fluoride (>1.5 ppm) causes fluorosis, affecting 200 million people, primarily in India and China, as of 2024.
Environmentally, fluorine compounds pose risks. Fluorinated gases, such as CFCs and HFCs, used in refrigeration, have high global warming potentials (up to 23,000 times that of CO₂). The 1987 Montreal Protocol phased out CFCs, reducing ozone depletion by 98% by 2025. However, HFCs remain a challenge, contributing 2% to greenhouse gas emissions. Conversely, fluorine’s role in pharmaceuticals is vital; 20% of drugs, including antidepressants like fluoxetine, contain fluorine, improving metabolic stability. Balancing these impacts requires careful regulation and innovation, ensuring fluorine’s benefits outweigh its drawbacks.

Leave a Reply