Introduction
Ever heard of argon gas uses? It’s a pretty cool topic! Argon, element 18, is this invisible noble gas. It lights up bulbs, keeps welds clean, and even helps in science experiments. Plus, it’s all around us in the air we breathe. As of May 2025, it’s still a big deal in tons of industries. This article’s gonna break down argon gas uses for you. We’ll check where it sits in the periodic table, its properties, how it was discovered, and what it does today. Ready to learn something new? Let’s dive in!
Argon’s actually the third most common gas in our atmosphere. About 0.93% of the air is argon—that’s more than you’d think! It’s been quietly doing its thing for centuries. So, how does it shape our lives? Stick around, and I’ll show you what makes this gas so awesome.

Where Does Argon Fit in the Periodic Table?
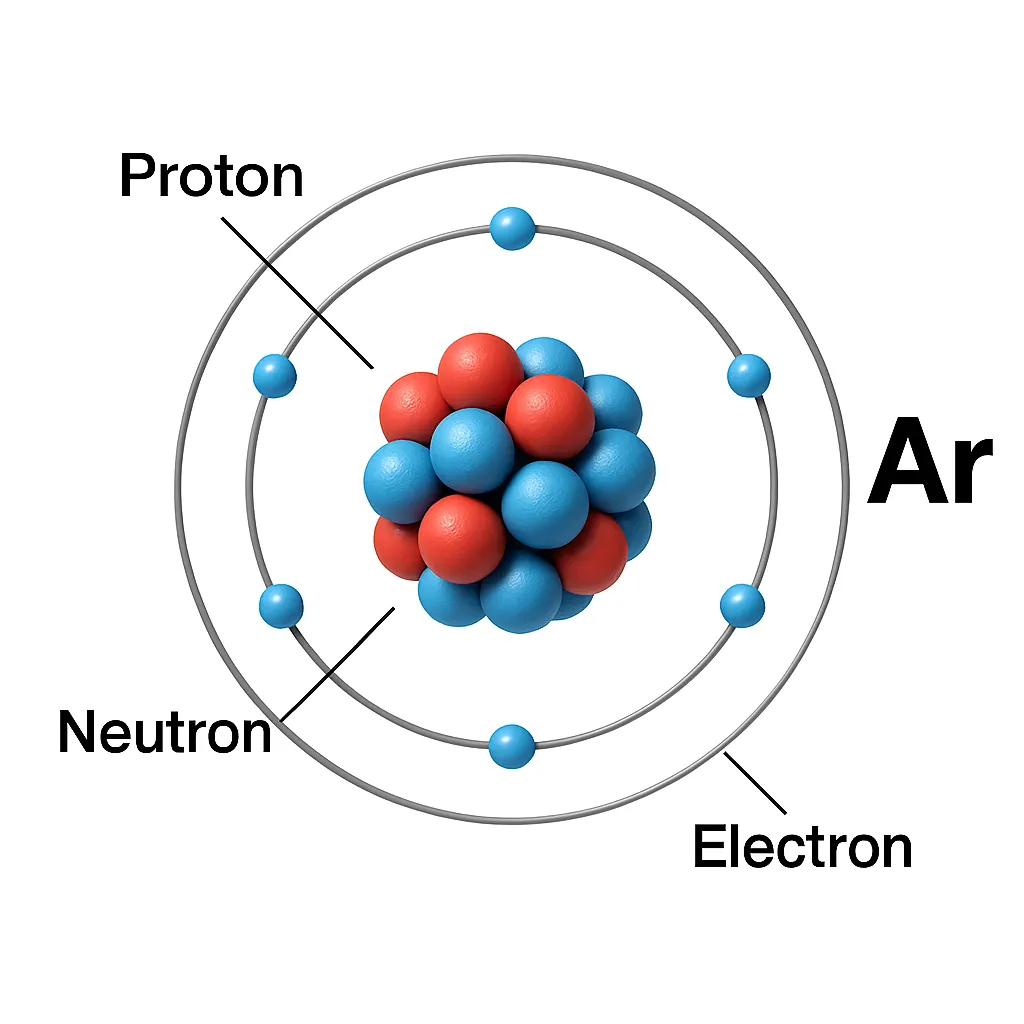
Argon in periodic table sits in Group 18 with other noble gases like helium, neon, and krypton. That means it’s got 18 protons and 18 electrons. Its electron setup is [Ne]3s²3p⁶, which makes it crazy stable. Basically, it doesn’t wanna react with anything—too chill for that! That’s why they call it “noble.” It’s like the introvert of the periodic table!
It makes up 0.934% of the air, more than carbon dioxide. Argon in periodic table shows up as argon-36 in space, but here on Earth, it’s mostly argon-40. That comes from decaying potassium-40 in rocks over millions of years. Fun fact: the sun has tons of argon too, formed during its fusion reactions. Its stability is what makes it perfect for so many uses. It even helps scientists study stars! Let’s take a closer look at its traits next.
What Are Argon’s Properties Like?
Argon properties are honestly kinda fascinating. It’s a colorless, odorless gas—no smell, no taste, nothing. You’d never even know it’s there! It melts at -189.3°C and boils at -185.8°C, so it’s only a liquid at super cold temps. Also, it’s heavier than air, with a density of 1.784 g/L. That means it can sink and pool up in low spots if it’s released in a room.
Here’s the cool part: argon properties make it super inert. Its outer electron shell is full, so it doesn’t react with much. Under extreme conditions, like at -256°C, it can form argon fluorohydride, but that’s super rare. In normal life, it just sits there, unbothered. It’s also 2.5 times more soluble in water than nitrogen, which is handy for some uses. Argon properties are why industries love it so much. It’s non-flammable and safe around sparks or flames. Let’s see how we found this sneaky gas!

How Was Argon Discovered?
Argon discovery history kicks off way back in 1785. A scientist named Henry Cavendish was messing around with air samples. He noticed about 1% of it wouldn’t react, no matter what he tried. But he couldn’t figure out what it was back then. Fast forward to 1894—that’s when Lord Rayleigh and William Ramsay finally cracked the mystery. They took air, removed the nitrogen and oxygen, and guess what was left behind? Argon!
They figured out that nitrogen from air was heavier than pure nitrogen. That little clue led them to this new gas. The name “argon” comes from a Greek word meaning “lazy”—perfect, since it doesn’t do much! Argon discovery history is a big deal in science. Rayleigh and Ramsay even won Nobel Prizes in 1904 for their work—one for Physics, the other for Chemistry. Their experiments changed how we see gases forever. How cool is that? Now, let’s talk about what argon does for us.

What Are Argon Gas Uses and Safety Tips?
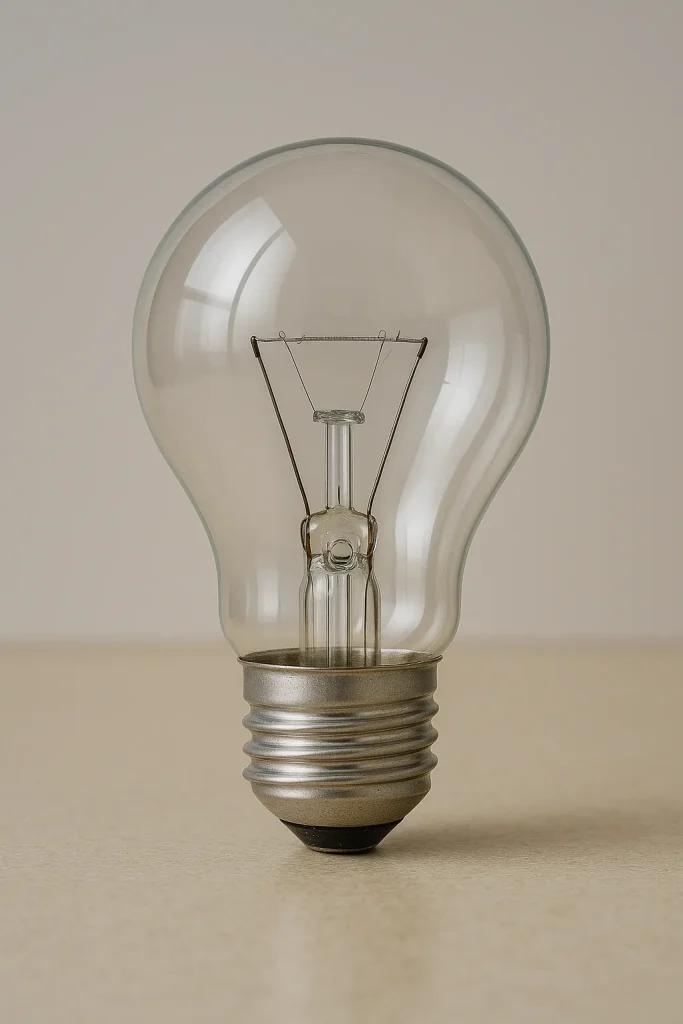
Argon gas uses are all over the place, and they’re super practical. First up, welders totally rely on it. They use argon as a shield to keep oxygen away from hot metals. That keeps welds clean and strong, especially for stuff like stainless steel or aluminum. It’s also in light bulbs—both old-school incandescent ones and modern fluorescent ones. Argon stops the filament from burning out too fast, so your bulbs last way longer.
But wait, there’s more! Argon gas uses include filling double-glazed windows. It traps heat between the glass panes, making your home cozy and saving energy on heating bills. In science, liquid argon is a big deal for experiments like neutrino research—super high-tech stuff! It’s also used in lasers that fix eye problems or zap tumors in medical treatments. And here’s a fun one: argon preserves old documents, like the Magna Carta, by keeping oxygen away so they don’t decay. It’s even used in winemaking to protect wine from oxidation during bottling and in food packaging to keep snacks fresh.
Now, let’s talk safety real quick. Argon’s non-toxic, so breathing a little is fine—it’s already in the air! But since it’s heavier than air, it can build up in low spots. In closed spaces, it might push out oxygen, which can make you dizzy or sleepy. Worst case, it could cause suffocation if there’s too much. So, store it away from heat, especially if it’s compressed in tanks. Labs use it in gloveboxes for air-sensitive work, but you gotta make sure it doesn’t pile up. Handle it smart, and these argon gas uses will keep making life better!

Leave a Reply