Introduction
Soil is that loose stuff on the ground where plants grow and critters live. It’s made up of bits like minerals, organic material, water, and air, all mixed together in different ways. Soil composition analysis looks at these parts to figure out what makes soil tick. It’s a big deal for farming and keeping the environment in check. This article dives into what soil is, what it’s made of, and why it’s not the same everywhere.
You’ll notice soils look and act differently depending on where you are. That’s because things like weather, rocks, and human activity shape them over time. Soil composition analysis helps sort out these differences. It’s all about getting a handle on how soil works in various places. Let’s break down the details step by step.

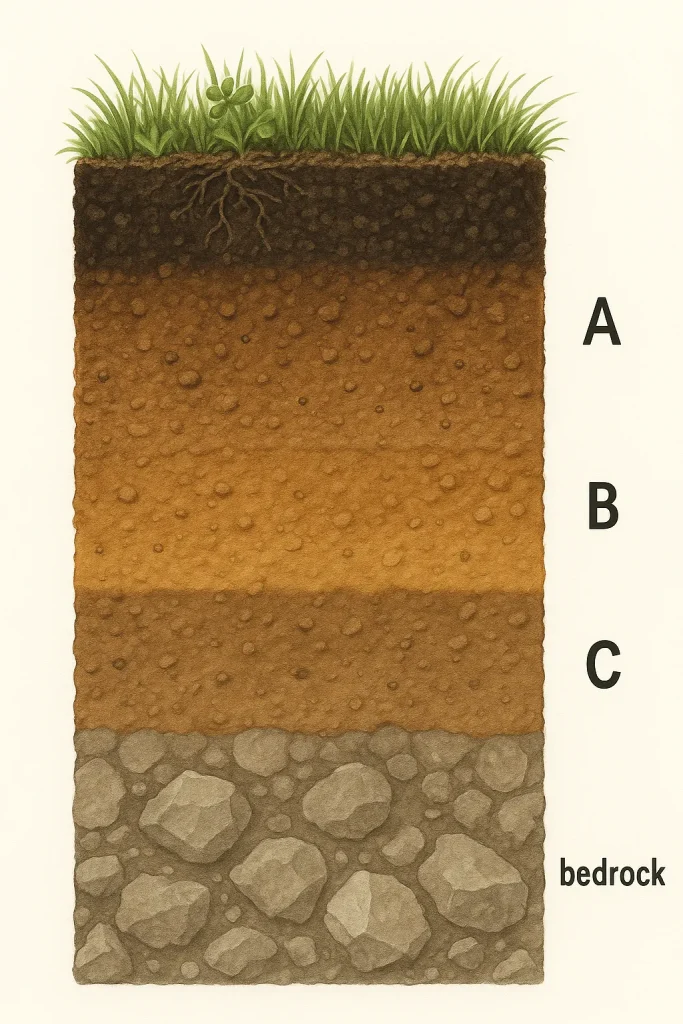
What Soil Is Made Of
Soil is a blend of mineral content, organic material, water, and air. The mineral content comes from rocks that break down into particles like sand, silt, or clay. Organic material is stuff like dead plants and animals that decompose and add nutrients. On average, soil might be about 45% minerals, 5% organic material, 25% water, and 25% air. Soil composition analysis measures these to see how soil supports plants.
Water in soil carries nutrients to plant roots, while air keeps roots and microbes breathing. If soil gets too packed, it loses air spaces, which makes it tough for plants to grow. Different soil types have different balances of these components. For instance, sandy soils let water pass through fast, but clay soils hold onto it. Each piece of the mix plays a part in how soil behaves.
Tiny organisms like bacteria and fungi live in soil, too. They break down organic material, making nutrients plants can use and keeping soil structure solid. The amount of water and air affects how active these microbes are. Soil composition analysis checks out these organisms to gauge soil health. All these elements together make soil a living system.

Why Soils Vary by Region
Soils aren’t the same everywhere because of things like climate, parent material, and terrain. Climate, like rain or heat, changes how fast rocks break down or how much organic material piles up. Wet, tropical areas often have clay-heavy soils, while dry deserts lean toward sandy ones. Soil composition analysis maps out these differences. It shows how local conditions shape what soil can do.
Parent material is the rock or sediment soil comes from. If it’s something like granite, the soil might be coarse and low on nutrients. Limestone, on the other hand, often makes richer, finer soil. Plants and animals in an area add their own touch, with forests leaving more organic material than grassy plains. These factors create all sorts of soil profiles around the world.
People also mess with soil through farming or building. Tilling too much can strip nutrients, and irrigation might make soil saltier. Soil composition analysis spots these changes and helps figure out how to fix them. By looking at regional factors, folks can adjust how they use land. That way, soils stay useful no matter where they are.
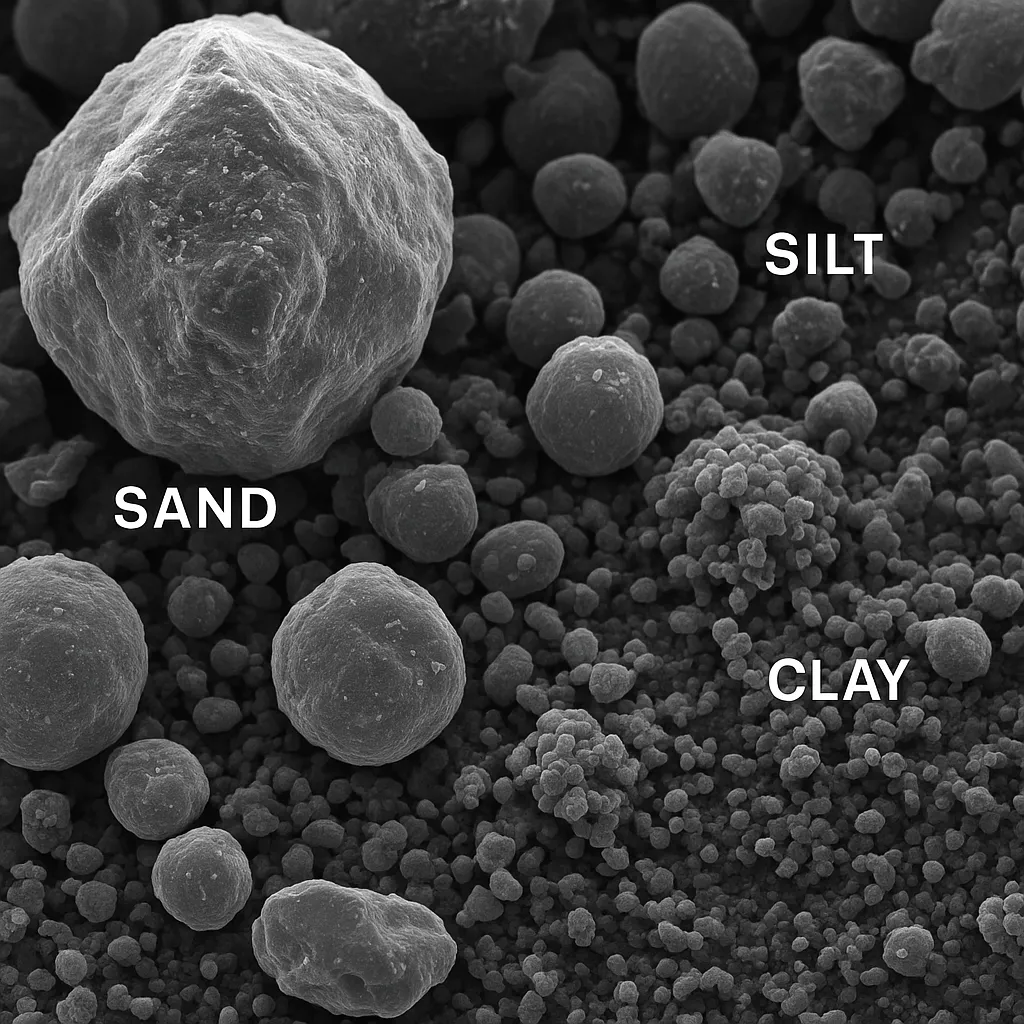

How Soil Texture Matters
Soil texture is about the mix of sand, silt, and clay particles. Sandy soils, with bigger particles, let water slip through but don’t hold nutrients well. Clay soils, with tiny particles, hang onto water but can get too dense. Soil texture affects how water moves, how much air is in there, and how roots spread out. Soil composition analysis uses texture to group soil types, like loam or silt.
Texture makes a difference for growing crops. Loamy soils, with a good mix of particles, work for most plants because they balance water and nutrients. Clay soils can drown roots if they stay too wet, so they need careful watering. Adding organic material can tweak texture, making sandy soils hold more water or clay soils drain better. Texture is a big factor in picking what to plant.
Farmers test soil texture with simple tricks, like feeling how it sticks together when wet. Soil composition analysis gives a clearer picture for things like watering or fertilizing. Sandy soils might need small, frequent doses of water, while clay soils do better with less often. Getting texture right helps soil do its job. It’s all about matching the soil to the task.

Dealing with Soil Differences
Handling different soils is tricky since they all have their own quirks. Some soils are naturally packed with nutrients, while others need extra help to grow anything. Regional soil variation means one-size-fits-all farming doesn’t cut it. Soil composition analysis pinpoints what each soil needs. That makes it easier to plan out how to use land without wrecking it.
Erosion and nutrient loss are big problems for soil. On hilly land, rain can wash away the good topsoil, leaving less fertile stuff behind. Farming the same crop over and over pulls out nutrients without putting any back. Things like planting cover crops or building terraces can stop erosion and keep nutrients in place. Soil composition analysis helps pick the right fix for the problem.
Farmers need tools like soil tests to know what’s going on underground. Tests show if the soil is short on mineral content or organic material, so people can add what’s missing. New tech, like machines that target exactly where to put fertilizer, helps use resources smarter. Working together, farmers and experts keep soils in good shape. It’s about making sure soil stays productive wherever it’s found.
Leave a Reply